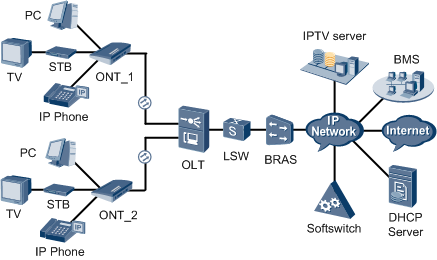
FTTH (Fiber to the Home) is a technology that connects optical fiber to a user’s home, which has developed rapidly over the past few years and is now the mainstream choice for broadband access worldwide.
In comparison with traditional broadband access technologies like DSL and cable TV, FTTH boasts higher bandwidth and lower latency. As the transmission speed of optical fiber is significantly faster than that of copper wire and coaxial cable, FTTH can offer a more stable and high-quality network experience. Simultaneously, FTTH also supports bidirectional communication, signifying that it can provide high-speed uplink and downlink speeds concurrently, better fulfilling users’ requirements for uploading and downloading data.
The development situation in different regions of the world is local. The Asian region has performed well in developing FTTH technology, with countries such as Japan, South Korea, and China having built large-scale fiber optic networks. South Korea, for example, has achieved nationwide FTTH coverage, with more than 90 percent of households having access to high-speed broadband services. In contrast, the development of FTTH in Europe and the United States is relatively backward, mainly due to the high construction cost and the restriction of market competition. In recent years, FTTH has been steadily increasing in popularity worldwide. According to statistics, more than a quarter of the world’s households have been connected to fiber optics. This trend will continue to accelerate, and FTTH will be more widely used and popularized.
In the future, FTTH technology will persist in evolving, and there are several tendencies worth observing. The first is the prevalence of ultra-high-definition video and virtual reality (VR). With the popularization of ultra-high definition videos such as 4K and 8K, conventional broadband fails to fulfill the bandwidth demands of users. The high-speed bandwidth of FTTH will turn into the infrastructure to support ultra-high-definition video and VR applications. Secondly, the ascent of the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G will further promote FTTH. The Internet of Things has emerged as a significant trend, with an increasing number of devices and applications requiring connection. The advent of 5G will bring about more data transmission requirements, and the low latency and high-speed bandwidth of FTTH will become the infrastructure of the 5G era. Additionally, with the rise of cloud computing, a growing number of applications and data will migrate to the cloud. The high-speed upload speed of FTTH will satisfy the needs of users for cloud storage and cloud applications, forming a complete cloud computing ecosystem.
The development of FTTH still faces some challenges. The first is the cost of construction. The construction cost of FTTH is relatively high, especially in areas with sparse population and complex geographical conditions. How to reduce the construction cost and expand the coverage of FTTH will be a problem to be solved. Second, there is the issue of competition. Although FTTH has advantages in bandwidth and performance, competitors such as cable providers and mobile operators are constantly improving their network speed and service quality. How to maintain competitive advantage in the competitive market will be the challenge that operators need to face.
Post time: Sep-12-2024